Jupyter Snippet CB2nd 06_ray
Jupyter Snippet CB2nd 06_ray
5.6. Optimizing Cython code by writing less Python and more C
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
w, h = 400, 400 # Size of the screen in pixels.
def normalize(x):
# This function normalizes a vector.
x /= np.linalg.norm(x)
return x
def intersect_sphere(O, D, S, R):
# Return the distance from O to the intersection
# of the ray (O, D) with the sphere (S, R), or
# +inf if there is no intersection.
# O and S are 3D points, D (direction) is a
# normalized vector, R is a scalar.
a = np.dot(D, D)
OS = O - S
b = 2 * np.dot(D, OS)
c = np.dot(OS, OS) - R * R
disc = b * b - 4 * a * c
if disc > 0:
distSqrt = np.sqrt(disc)
q = (-b - distSqrt) / 2.0 if b < 0 \
else (-b + distSqrt) / 2.0
t0 = q / a
t1 = c / q
t0, t1 = min(t0, t1), max(t0, t1)
if t1 >= 0:
return t1 if t0 < 0 else t0
return np.inf
def trace_ray(O, D):
# Find first point of intersection with the scene.
t = intersect_sphere(O, D, position, radius)
# No intersection?
if t == np.inf:
return
# Find the point of intersection on the object.
M = O + D * t
N = normalize(M - position)
toL = normalize(L - M)
toO = normalize(O - M)
# Ambient light.
col = ambient
# Lambert shading (diffuse).
col += diffuse * max(np.dot(N, toL), 0) * color
# Blinn-Phong shading (specular).
col += specular_c * color_light * \
max(np.dot(N, normalize(toL + toO)), 0) \
** specular_k
return col
def run():
img = np.zeros((h, w, 3))
# Loop through all pixels.
for i, x in enumerate(np.linspace(-1, 1, w)):
for j, y in enumerate(np.linspace(-1, 1, h)):
# Position of the pixel.
Q[0], Q[1] = x, y
# Direction of the ray going through
# the optical center.
D = normalize(Q - O)
# Launch the ray and get the color
# of the pixel.
col = trace_ray(O, D)
if col is None:
continue
img[h - j - 1, i, :] = np.clip(col, 0, 1)
return img
# Sphere properties.
position = np.array([0., 0., 1.])
radius = 1.
color = np.array([0., 0., 1.])
diffuse = 1.
specular_c = 1.
specular_k = 50
# Light position and color.
L = np.array([5., 5., -10.])
color_light = np.ones(3)
ambient = .05
# Camera.
O = np.array([0., 0., -1.]) # Position.
Q = np.array([0., 0., 0.]) # Pointing to.
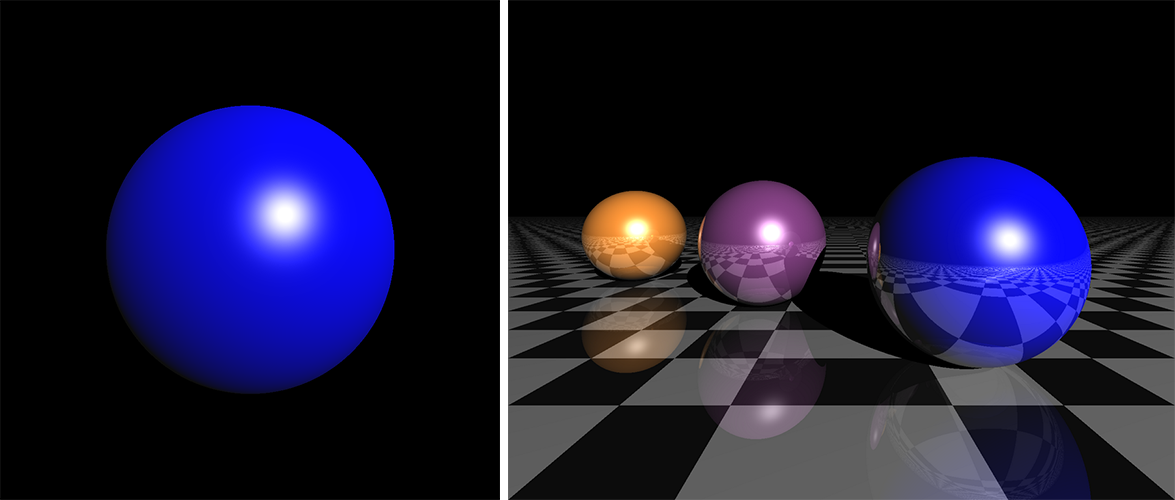
img = run()
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 10))
ax.imshow(img)
ax.set_axis_off()
%timeit run()
2.75 s ± 29.9 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs,
1 loop each)
import numpy as np
cimport numpy as np
DBL = np.double ctypedef
np.double_t DBL_C
from libc.math cimport sqrt
cdef normalize(np.ndarray[DBL_C, ndim=1] x):
cdef double n
n = sqrt(x[0]*x[0] + x[1]*x[1] + x[2]*x[2])
x[0] /= n
x[1] /= n
x[2] /= n
return x
cdef tuple add(tuple x, tuple y):
return (x[0]+y[0], x[1]+y[1], x[2]+y[2])
cdef struct Vec3:
double x, y, z
cdef Vec3 vec3(double x, double y, double z):
cdef Vec3 v
v.x = x
v.y = y
v.z = z
return v
cdef Vec3 add(Vec3 u, Vec3 v):
return vec3(u.x + v.x, u.y + v.y, u.z + v.z)