Jupyter Snippet CB2nd 04_turing
Jupyter Snippet CB2nd 04_turing
12.4. Simulating a partial differential equation — reaction-diffusion systems and Turing patterns
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
a = 2.8e-4
b = 5e-3
tau = .1
k = -.005
size = 100 # size of the 2D grid
dx = 2. / size # space step
T = 9.0 # total time
dt = .001 # time step
n = int(T / dt) # number of iterations
U = np.random.rand(size, size)
V = np.random.rand(size, size)
def laplacian(Z):
Ztop = Z[0:-2, 1:-1]
Zleft = Z[1:-1, 0:-2]
Zbottom = Z[2:, 1:-1]
Zright = Z[1:-1, 2:]
Zcenter = Z[1:-1, 1:-1]
return (Ztop + Zleft + Zbottom + Zright -
4 * Zcenter) / dx**2
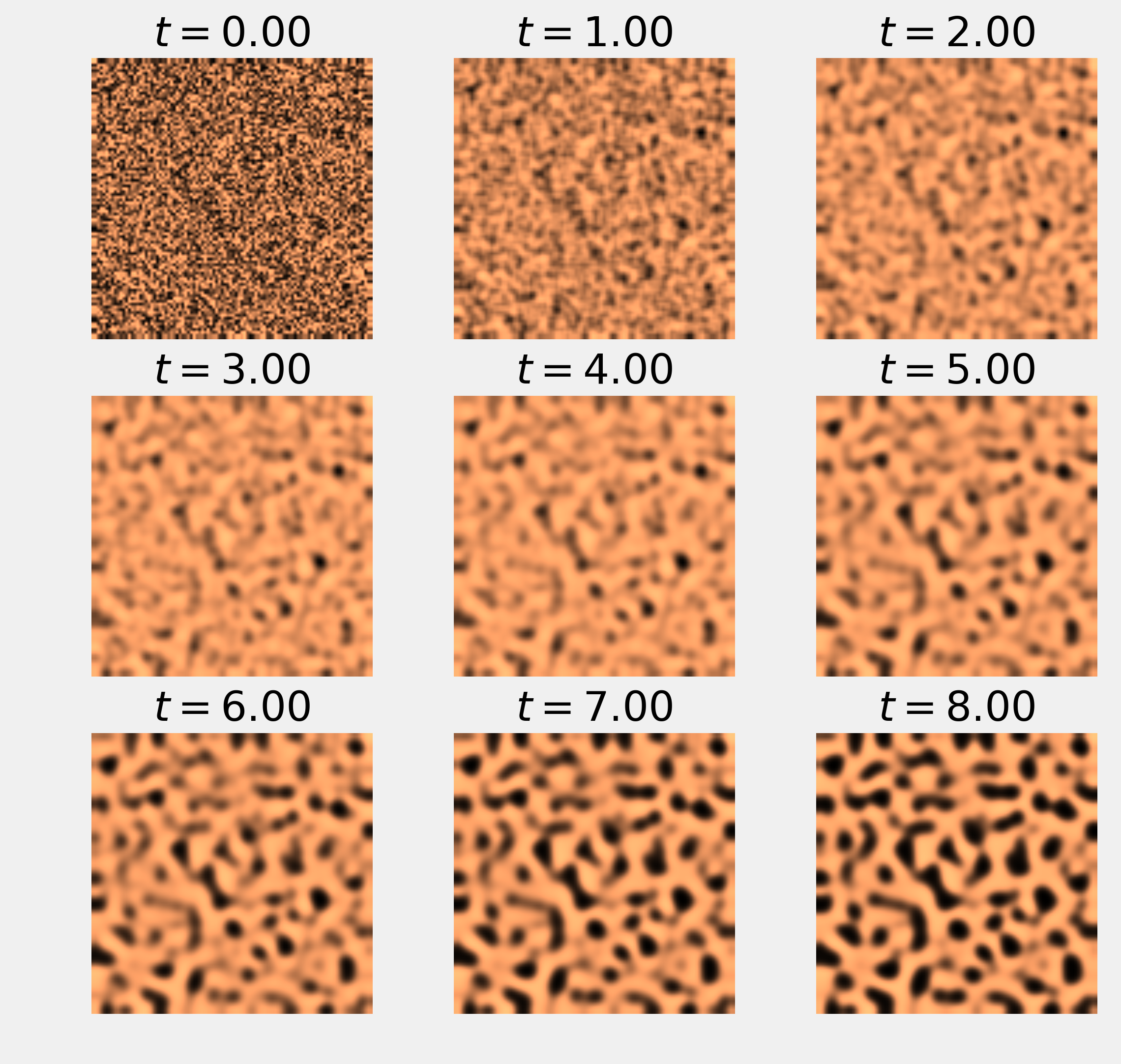
def show_patterns(U, ax=None):
ax.imshow(U, cmap=plt.cm.copper,
interpolation='bilinear',
extent=[-1, 1, -1, 1])
ax.set_axis_off()
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 3, figsize=(8, 8))
step_plot = n // 9
# We simulate the PDE with the finite difference
# method.
for i in range(n):
# We compute the Laplacian of u and v.
deltaU = laplacian(U)
deltaV = laplacian(V)
# We take the values of u and v inside the grid.
Uc = U[1:-1, 1:-1]
Vc = V[1:-1, 1:-1]
# We update the variables.
U[1:-1, 1:-1], V[1:-1, 1:-1] = \
Uc + dt * (a * deltaU + Uc - Uc**3 - Vc + k),\
Vc + dt * (b * deltaV + Uc - Vc) / tau
# Neumann conditions: derivatives at the edges
# are null.
for Z in (U, V):
Z[0, :] = Z[1, :]
Z[-1, :] = Z[-2, :]
Z[:, 0] = Z[:, 1]
Z[:, -1] = Z[:, -2]
# We plot the state of the system at
# 9 different times.
if i % step_plot == 0 and i < 9 * step_plot:
ax = axes.flat[i // step_plot]
show_patterns(U, ax=ax)
ax.set_title(f'$t={i * dt:.2f}$')
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 8))
show_patterns(U, ax=ax)
